Predictive Maintenance: A Paradigm Shift in Asset Optimization
Published Nov. 19, 2024, 10:46 a.m. by Ezra Ogori
Predictive Maintenance (PdM) has emerged as a pivotal strategy in asset management, enabling industries to optimize equipment lifespan, reduce downtime, and lower maintenance costs. Unlike preventive maintenance, which relies on predetermined schedules, predictive maintenance employs data-driven insights and advanced analytics to predict equipment failures before they occur.
In this blog, we delve into the nuances of predictive maintenance, differentiate it from preventive maintenance, explore its techniques, outline its implementation steps, and highlight its benefits.
Predictive vs. Preventive Maintenance
| Aspect | Predictive Maintenance | Preventive Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Monitors equipment using real-time data to predict failures. | Maintains equipment based on fixed schedules. |
| Approach | Condition-based and data-driven. | Time-based and rule-driven. |
| Data Utilization | Utilizes IoT sensors, historical data, and advanced analytics. | Rarely relies on extensive data; primarily follows manufacturer recommendations. |
| Cost | High initial cost but cost-effective in the long run. | Moderate cost but risks over-maintenance or under-maintenance. |
| Downtime | Minimizes unplanned downtime. | May lead to unnecessary downtime due to rigid schedules. |
| Application | Best for critical, high-value equipment. | Suitable for less complex, lower-cost equipment. |
Techniques Used in Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance integrates diverse technologies to monitor, analyze, and predict equipment health:
| Technique | Description | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Vibration Analysis | Measures vibration patterns to detect misalignments or wear in machinery. | Rotating machinery (e.g., motors, pumps). |
| Infrared Thermography | Uses thermal imaging to identify heat anomalies. | Electrical systems, bearings. |
| Ultrasound Analysis | Detects high-frequency sound waves caused by leaks or mechanical wear. | Compressed air systems, gearboxes. |
| Oil Analysis | Examines lubricant properties to identify contamination or degradation. | Hydraulic systems, gearboxes. |
| Machine Learning Models | Processes historical data to predict failure probabilities. | Industrial IoT systems. |
| IoT Sensors | Provides real-time monitoring of temperature, pressure, and other critical parameters. | High-value assets in manufacturing plants. |
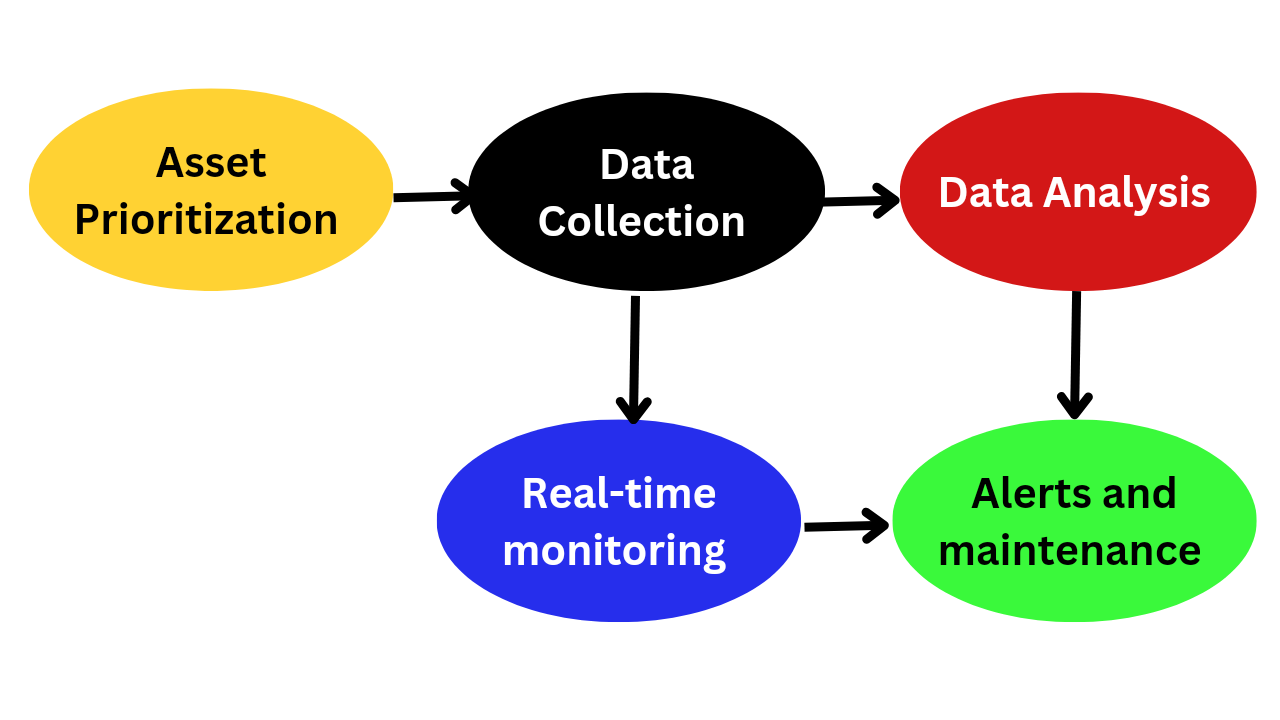
Implementation of Predictive Maintenance
Implementing predictive maintenance involves a step-by-step process. Below is an illustrated guide to the implementation strategy:
1. Define Objectives
- Identify critical equipment.
- Set goals such as reducing downtime or optimizing costs.
2. Collect Data
- Deploy IoT sensors to monitor key parameters (e.g., vibration, temperature).
- Gather historical performance data.
3. Analyze Data
- Use advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms to assess equipment health.
4. Develop Predictive Models
- Train models using historical data to identify failure patterns.
5. Implement Monitoring Systems
- Integrate systems for real-time equipment monitoring.
6. Create Alerts
- Configure alerts for potential failures based on model outputs.
7. Act on Insights
- Perform maintenance when alerts indicate imminent failures.
Implementation Flowchart
Below is a flowchart illustrating the implementation process:
Benefits of Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance offers a myriad of benefits, transforming asset management:
- Reduced Downtime: Proactively addresses issues before failures occur, minimizing interruptions.
- Cost Efficiency: Lowers maintenance costs by avoiding unnecessary repairs.
- Extended Equipment Life: Enhances equipment longevity through timely interventions.
- Improved Safety: Identifies risks early, preventing hazardous situations.
- Optimized Resource Allocation: Focuses efforts on critical issues, reducing manpower wastage.
Real-World Example
In the manufacturing sector, a company implemented predictive maintenance for its conveyor systems. Using vibration sensors and machine learning, the company reduced unplanned downtime by 40% and achieved annual savings of $500,000 in maintenance costs.
Conclusion
Predictive maintenance is a game-changer for industries aiming to stay competitive in today’s fast-paced environment. By leveraging data and advanced analytics, organizations can maximize efficiency, minimize costs, and ensure equipment reliability. Transitioning to predictive maintenance is not just a technological shift but a strategic investment in operational excellence.
Whether you’re in manufacturing, energy, or transportation, the question is no longer if you should adopt predictive maintenance but when.
pHqghUme Sept. 20, 2025, 8:54 p.m.
Zjz0Avn4